
BME offers infrastructure and assistance within microfluidics, acoustofluidics, and microfabrication. We can design and develop microsystems for processing of body/bodily fluids, cell sorting, immobilization, and neural electrodes.

Contact Martin Bengtsson to discuss the feasibility of a potential Life Science Microfluidics project.
martin.bengtsson@bme.lth.se
To apply for a project, please use the form here:
Access request form
Examples of available technology and past projects:
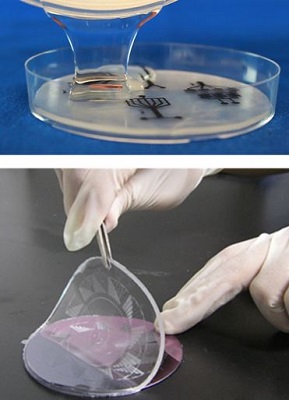
We can work with PDMS/silicone, thermoplastics (polypropylene, polyimide etc), glass, aluminum.
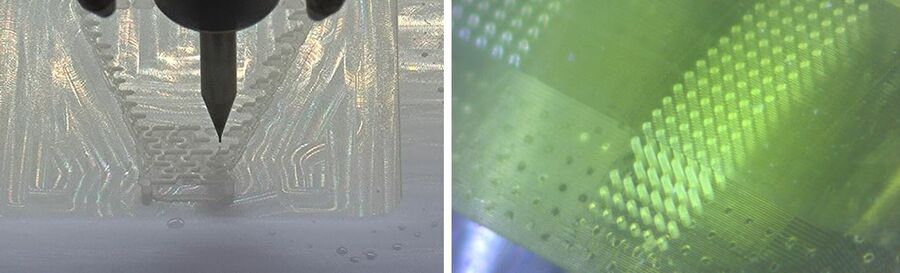
Micromilling down to 50 µm. Photolitography down to 5 µm. 3D-printing: Extruder, SLA (400 µm), DLP (10 µm features, 2 µm spots, 5 µm layers). Silicon and glass microfabrication.
Equipment examples: (external links)
Boston Microfabrication MicroArchS230 - https://bmf3d.com/2μm-series-3d-printers/
SLA (stereo lithography) printer - https://formlabs.com/eu/3d-printers/form-2/
Datron Neo Series 2 (Swedish link)- https://www.solectro.se/Product/Index/6977
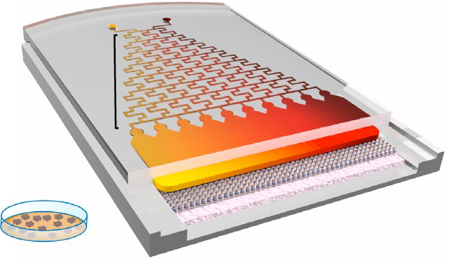
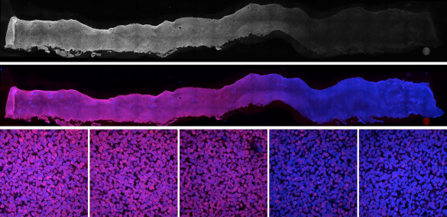
Gradient generator for Stem Cell regionalisation
Modeling neural tube development by differentiation of human embryonic stem cells in a microfluidic WNT gradient
Nature Biotechnology | VOL 38 | November 2020 | 1265–1273.
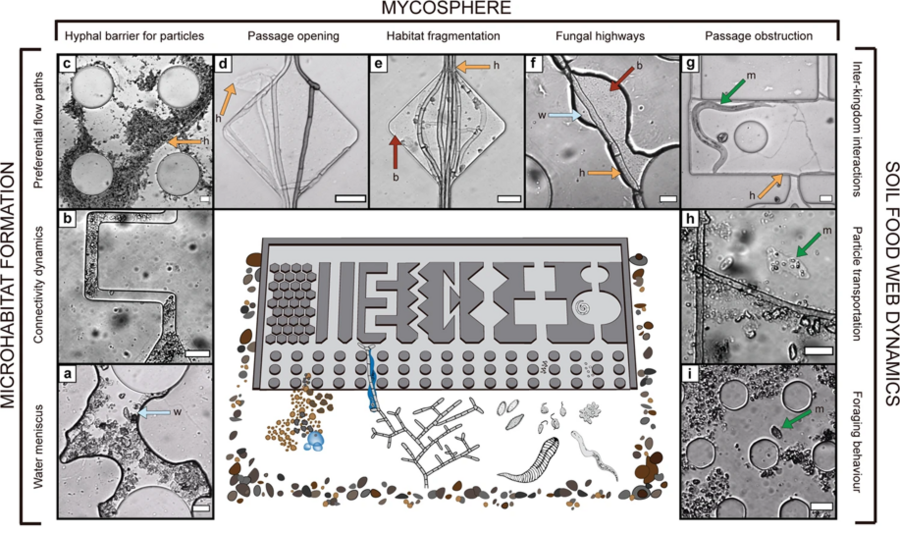
Microfluidic chips provide visual access to in situ soil ecology, COMMUNICATIONS BIOLOGY | (2021) 4:889
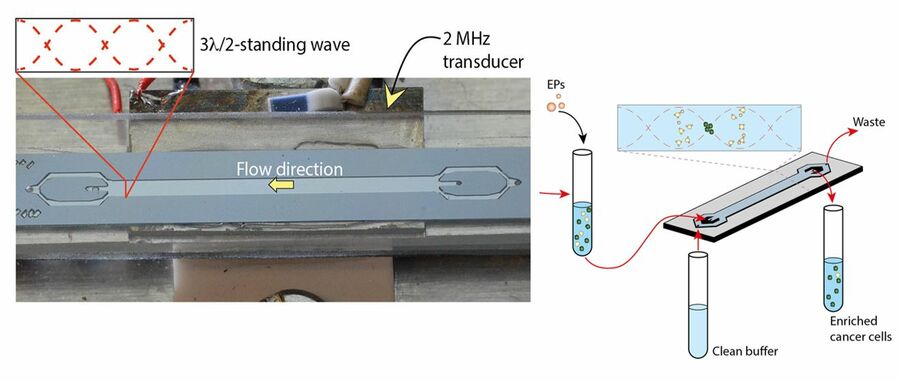
Two-Step Acoustophoresis Separation of Live Tumor Cells from Whole Blood (2021) In Analytical Chemistry 93(51). p.17076.
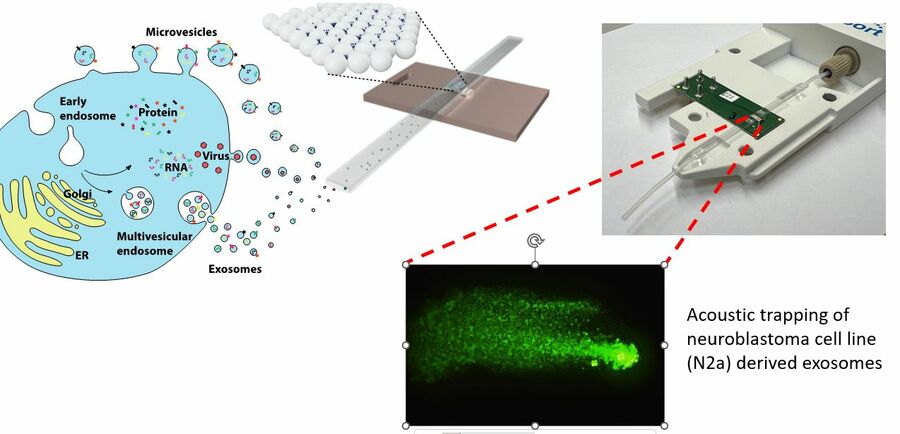
Acoustic nanoparticle trapping enables isolation and purification of extracellular vesicles in samples as small as e.g. 10 µL blood plasma.
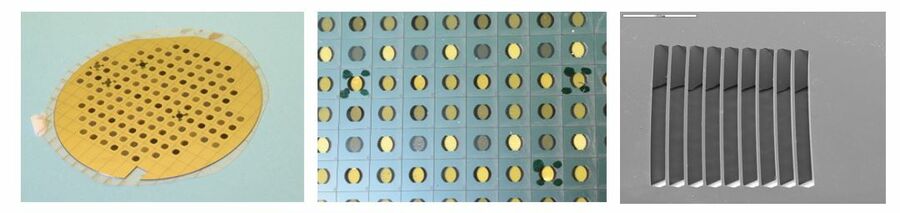
Biogrid—a microfluidic device for large-scale enzyme-free dissociation of stem cell aggregates, Lab Chip, 2011, 11, 3241
Page Editor: tord.hjalt@bme.lth.se
Managers
Project group
Axel Tojo, Martin Bengtsson, Johan Nilsson, Thomas Laurell.


